TPM 2.0 Technology: Premio’s Cybersecurity Armor for Connected Computing
Embedded and rugged edge compute systems collecting and processing sensitive data become targets for cyberattacks as they connect to the IoT. Intellectual property, personal data and machine commands become increasingly susceptible to exfiltration or manipulation with increased connectivity. To protect its systems — as wells as the people, products and services dependent on their security — Premio integrates trusted platform modules (TPMs) with TPM 2.0 standards. Learn more about TPM 2.0 for IoT

Security Standard
TPM 2.0 is the international standard for microcontrollers dedicated to hardware security.

Discrete Module
The tamper-resistant TPM cryptoprocessor is physically connected to the motherboard.

IoT Core Edition
Control access to protected data at connected endpoints and cloud interfaces.

Trusted Platform Module 2.0
TPM standards ensure secure data storage, as well as platform authentication and integrity auditing. TPM 2.0’s three hierarchies permit multiple root keys for improved security over TPM 1.2 standards. This provides better resistance to malware and rogue applications affecting legitimate processes.

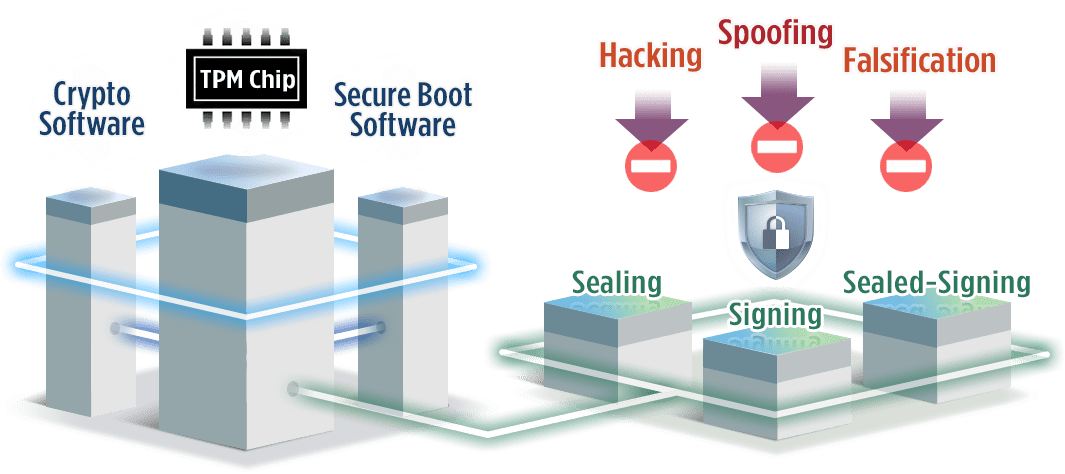
TPMs scan BIOS to detect unauthorized changes to the system.
The TPM locks the system when the hard drive is unexpectedly relocated.
The TPM can enable BitLocker Drive encryption to determine if conditions are safe for booting.

TPM Features
- Safeguards data with a secure hardware-integrated algorithm
- Protects against hackers, malware and physical theft
- Resists brute force decryption attack
- Generates quality random numbers
- Provides support for encryption in the platform
- Establishes platform identities
- Store keys and data
- Signs and verifies digital signatures
- Audits key usage and data access



