The advancements in connectivity fueling the digital IoT transformation are uncovering new surveillance potential for many organizations. This potential has also elevated the accountability for many organizations tasked with ensuring public safety and property security. As a result, organizations are deploying nimble, high-resolution IP cameras and NVRs at network edges to broaden their visual awareness of the environments for which they are responsible. Many public service, business and manufacturing sectors have strict mandates for the maintaining a suitable surveillance system, with some regulations even specifying frame rates and resolutions that ensure accountability for safety and quality. With IP camera technology’s leaps in improvement and the lowering cost of system ownership, there’s little excuse for failing to adequately monitor surroundings.
According to research and advisory firm Gartner, outdoor surveillance cameras will be the largest market for 5G IoT through the next three years. Seventy percent of IoT endpoints deployed will be dedicated to rugged surveillance as city operators tasked with the safety and security of public spaces and buildings make up the bulk of the addressable market. These cameras, however, would be limited to out-of-the-box functionality without robust edge NVRs collecting and processing the video data at the surveilled location.

How Has Edge Surveillance Evolved?
When IP camera technology began overtaking analog in surveillance installations, the concept of decentralized “edge surveillance” involved autonomous cameras with onboard computing, analysis and storage to process data and undertake functions pertinent to the camera’s intended mission. This could be facial recognition, motion detection or infrared vision with onboard storage. These cameras were remotely placed, independent of the NVR at the heart of the main centralized system.
As NVR video analytics and machine learning evolved and overshadowed the limited functionality of edge cameras, many organizations realized the value of aggregating and leveraging video data with NVR-backed processing power at the surveilled edge locations. By moving the NVR closer to many of the camera’s real-time video data feeds, bandwidth could be spared and latency avoided by the proximity. Deploying traditional NVRs at the edge, however, was easier said than done for remote, volatile and/or moving environments. This is where rugged NVR computers take over and provide valuable workload consolidation at the edge.
What’s the Difference Between a Rugged NVR and a Traditional NVR?
In the simplest terms, anything a traditional NVR can do, a rugged NVR computer can do but has been validated for harsh environments. In terms of mechanical form factor, a traditional NVR is not designed for the physical and logistical challenges present at many edge surveillance deployments. Traditional NVRs were intended to perform in stable, easily-controlled locations.
Purpose-built rugged NVR computers today leverage high-performance GPU cores to render visual inference analysis backed by machine-learning algorithms. Rugged NVR computer applications use both robust sequential and parallel compute for biometric identification (including facial recognition), license plate recognition, behavioral detection, traffic flow optimization and virtually any other application leveraging inference of captured video data.
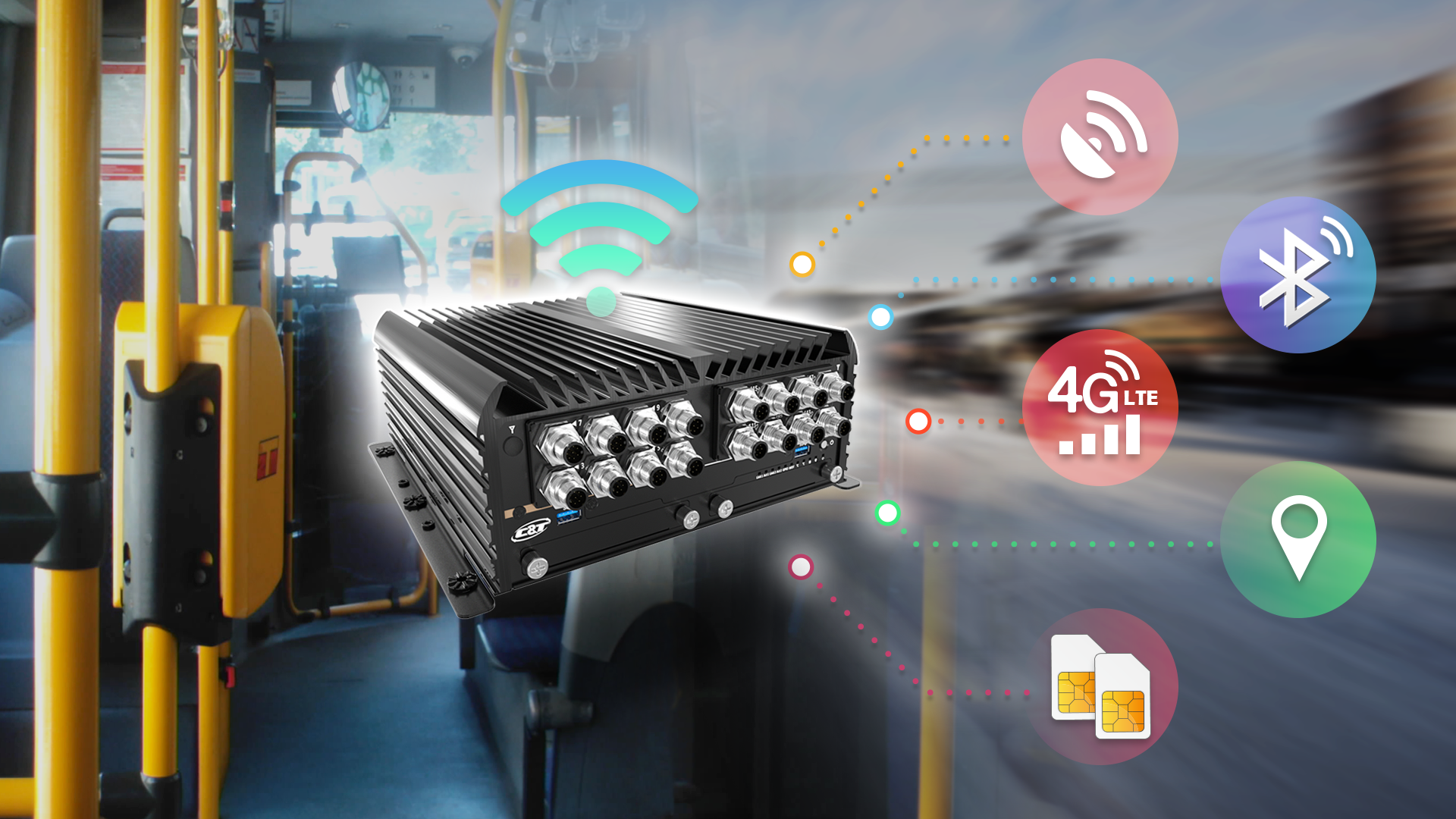
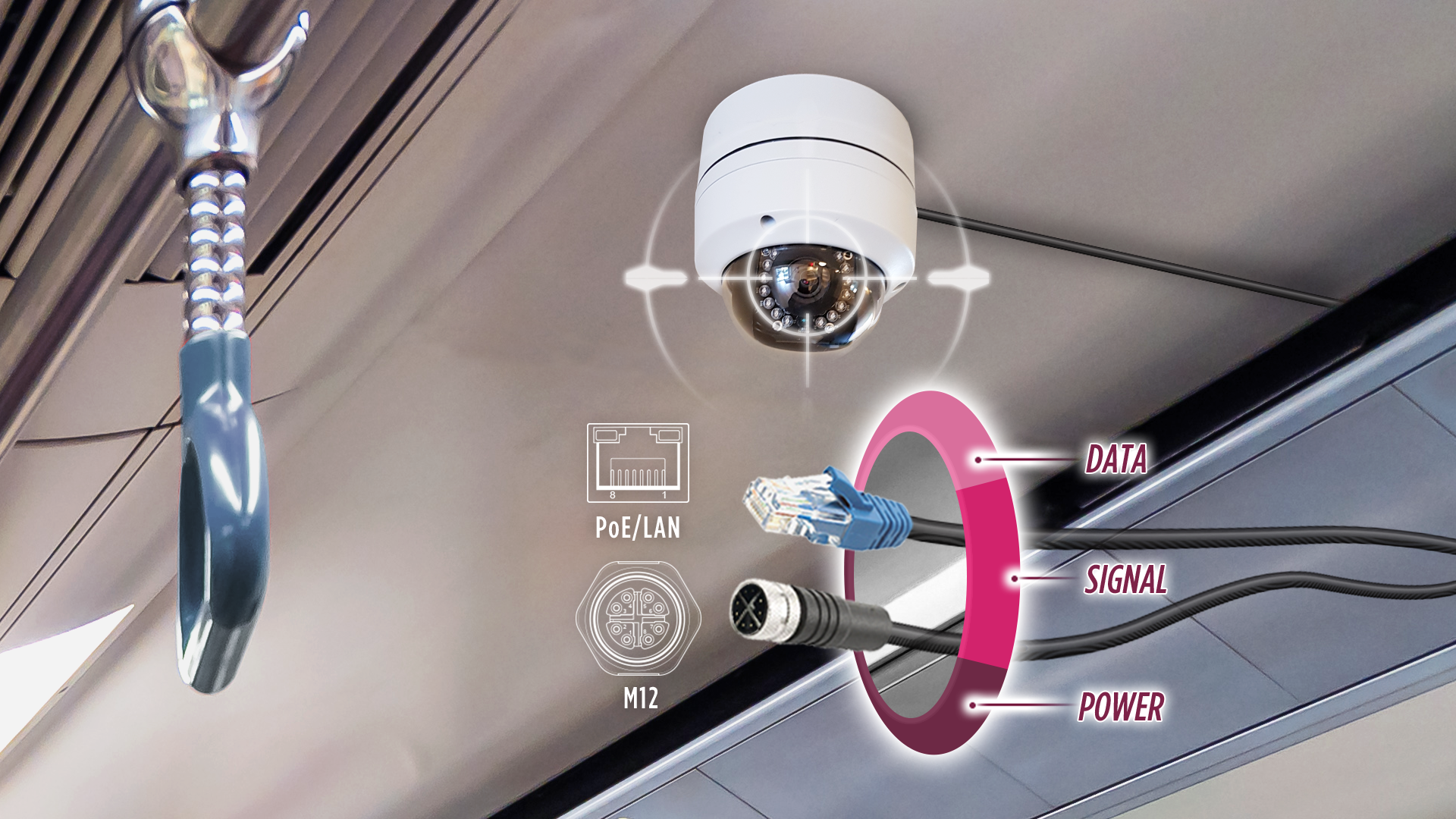
Another distinct feature rugged NVR computers provide is support for PoE+ connectivity. Many modern surveillance deployments benefit from PoE/PoE+ cameras because of the ability to transmit power, video data and signals with a single CAT5 cable. The PoE+ connectivity also enables integration of other resource-constrained IoT security peripheral devices like those used for access control, alarms, beacons and event-response systems.
But the main difference of rugged NVR computers is their ability to deliver mission-critical reliability in rigorous and harsh environments that traditional NVRs cannot endure. Rugged NVR computers are purpose-built to deliver keen visual processing and recording at locations with constant or intermittent vibration and movement, contaminants, questionable power voltages and severe temperature conditions. As more and more IoT devices communicate valuable data, rugged NVR computers play a pivotal role for mobile and remote surveillance at the edge in real time.
Wide-Operating Temperature for harsh edge deployments (-40C to 70C)
Fanless Passive Cooling Technology
Five Innovations Behind Rugged NVR Computer Design
Rugged NVR computers are designed with longevity in mind. For rugged edge deployments, this means validating specific scenarios that could jeopardize critical workload operations. To accommodate, embedded computer manufactures specialize in edge computing designs eliminating multiple points of failures.
1. Passive cooling technology eliminates the need for an active fan — a common point of failure for computers. With better means of regulating temperature, fanless computers remove the need for vents that often permit dust, pollutants and fluids to penetrate the case and damage critical electronics within.
2. Rugged NVR computers need to be rated to withstand shock, movement and vibrations inherent to many industrial and in-vehicle deployments. They should also have a wide operating temperature to withstand extreme outdoor deployments or industrial environments with severe temperatures. Rugged NVR computers deployed in environments with wet conditions must be rated for either IP65 or IP67 liquid resistance according to exposure.
3. Wide voltage input (9- 50 VDC) allows the devices to operate with uncertain or fluctuating power sources, providing some resistance to electrical surges. Also, some rugged NVR computers used in railway, public transportation, and trucking have a power ignition management function to run off 12-24VDC car batteries.
4. Rugged NVR computers need great wireless flexibility for remote and mobile deployments. 4G/LTE technology and SIM modules will give appliances clear connectivity to cloud resources or other systems. These make rugged NVR computers ideal for remote and in-vehicle deployments as appliances to maintain continuous connectivity despite location. Mobile broadband connectivity like 4G/LTE (and eventually 5G) enables vehicle-to-everything (V2X) transmissions that can provide GPS and telematics data, and alert operators to traffic, detours or hazardous conditions in real time. Additionally, a rugged NVR computer outfitted with Bluetooth technology may integrate high-speed sensor and device data into the surveillance or operations deployments.
5. A trusted platform module (TPM) with TPM 2.0 technology can provide foundational protection for the hub of the edge surveillance system. Discrete TPM cryptoprocessors installed by embedded computing manufacturers secure the hardware level, offering boot security that prevents successful injection of malware capable of affecting surveillance system performance. TPMs also enable encryption on IoT computers, preventing exposure of video and accompanying data to unauthorized parties. These protections can help organizations comply with numerous data privacy controls like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Health Insurance Portability Accountability Act (HIPAA) and several industry compliance regulations.

Who Needs a Rugged NVR Computer?
As the world of IoT connectivity expands, so too expands the number of surveillance deployments that traditional NVR technology was not built to sustain. Rugged NVR computers were designed for endurance and longevity to adequately monitor, record and process visual data in physically punishing industrial, remote, mobile and outdoor environments.
Popular Deployments of Rugged NVR Computers
- Smart factories and critical infrastructure undergoing digital transformation require agile recording hardware with a lifespan that mirrors those of the legacy equipment and cyberphysical systems populating the manufacturing zone, gleaning valuable performance insights in the process.
- First-responder vehicles need mobile video recording that can wirelessly capture body cam and dash video, push information to headquarters and other responders, and survive the impact of a PIT maneuver.
- Unmanned airport security touchpoints tasked with ensuring traveler identity for secure passage can leverage strong GPU inference analysis toward rapid, accurate facial recognition and possess the durability to withstand heavy luggage collisions.
- Railways and logistic trucking organizations using in-vehicle cameras for passenger safety and incident logging can also push rich telematics data containing location, speed and fuel consumption back to central operation centers for more efficient fleet management.
But the rugged NVR computer shouldn’t be restricted to inhospitable environments. Many organizations are plagued with budget limitations that are felt most in the safety and security realms. These organizations often prioritize longevity in their surveillance buying decisions, and a rugged NVR computer can extend MTBF and generate business insights and performance optimizations for a quicker ROI.