An industrial computer is a specific type of computing system engineered to manage a variety of factory and industrial workloads for machine automation, manufacturing equipment and new-age autonomous robotics. One major benefit from industrial computers is the ability to operate with high reliability in the harshest industrial environments. Most industrial computers share rugged design concepts that utilize fanless cooling technology, cableless connections to eliminate moving parts, and resistance to some level of dust and water intrusion. These key characteristics are some of the greatest advantages for industrial computers because it provides stability and efficiency for many industrial automation deployments that are unable to afford downtime.
How is an Industrial Computer Different Than a Commercial Desktop Computer?
Commercial Dell Desktop Computer
An industrial computer is different from a commercial desktop computer in very specific ways due to its deployment use cases. Although the internal components may seem like ordinary desktop computer components, (CPU, Memory, Storage); but an industrial computer is very different in its distinct rugged design features that are engineered for reliability and precision in industrial automation machines. There are many design features that are integral to the performance and stability of industrial computers that you should compare and evaluate to ensure the best total cost of ownership when integrating computing hardware:
-
Enclosure form factor: It is common for industrial computers to undergo harsh factory conditions where exposure to wide temperatures, vibration, and voltage spikes can cause harm to a general computer. Therefore, industrial computers have internal components made from alloy materials that are strong enough to withstand high temperatures and vibrations. Most external enclosures feature a robust aluminum chassis that acts as a heat sink that transfers heat away from critical internal components like the central processing unit, memory, and storage.
-
Industrial Grade Components: Industrial computers will often times feature industrial grade components that have been tested and validated to operate in harsh industrial environments. Everything from the PCB motherboard to the electrical soldered capacitors are specifically chosen and integrated into a final industrial computer design that is ready for mass deployment in factory settings.
-
Protection from Dust and particulate intrusion: Industrial computers are designed specifically for deployment in areas such as factory automation or mining processes where dust and foreign debris is often a common companion. Therefore, industrial computers are designed with rugged design features that eliminate the need for cooling vents, preventing dust and other particulates in harsh environments to jeopardize the computer and its functionality.
-
Extreme temperature: Many industrial applications require computers capable of withstanding extreme operating temperatures. Since computers with fans are subject to failure from dust contamination, these specialized computers are designed with a fanless system architecture that utilizes heat sinks and heat pipes to maintain wide operable temperatures. This allows industrial computers to function in harsh environments and where temperatures is often uncontrollable. For example, computers in industrial use cases can support operating temperatures from –40C to 70C (-40F to 158F), allowing functionality in both extreme cold and hot applications.
-
Shock and Vibration Resistance: High levels of shock and vibration can be detrimental to a computer that has not undergo extensive design validation and testing. Most industrial computers will feature some level of resistance to these environmental factors and maintain functionality during these specific situations. For example, some industrial automation equipment can create levels of shock and vibration during the manufacturing process that may cause harm to general computers and causing system failures. Support for vibrations levels range from 3-5 GRMS; and shock is often support up to 50G; some industrial computers also can meet stringent military specifications like MIL-STD-810G, for heavy duty military use cases.
- Ingress Protection (IP Ratings): Not only are industrial computers dust proof, they can also be water-resistant to a certain degree. The key for a reliable and rugged computer is to eliminate multiple points of failures, especially from dust and water elements. For example, in industrial applications such as food manufacturing and chemical processing, automation equipment and its computers are often washed down with heated water jets or cleansing materials. Therefore, most industrial computers used in those settings have some levels of IP protections from the design to even special M12 connectors, which will be explained below.
-
EMI resistance: Short for electromagnetic interference (EMI), a naturally occurring phenomena generated when the electromagnetic (EM) field of one device degrades the EM field of another device in proximity. This can lead to the degradation of circuits and may even stop it from functioning. In industrial settings where the existence of different equipment combined with inadequate installations could facilitate the emission of unwanted EM disturbances and causing signal interference. Therefore, most industrial computers are properly designed, shielded, and tested to ensure complete isolation and adhere to strict regulatory standards and compliance.
- Expandability and Longevity: Industrial computers have more expansion capabilities than commercial computers to include proper support for many legacy devices and applications. Many of the components used are available and can last up to 15 years, providing a embedded computing solution for the long-term. This is especially important for industrial factories that may not have the ability to upgrade or retrofit with the latest automation technology every few years. Therefore, most industrial computers today provide a platform to help consolidate multiple workloads that derive from various legacy and up-to-date technological features. One key example is the ability to support legacy analog serial ports versus the latest digital universal serial bus (USB) connectors.

Most Popular I/O Ports Made for Industrial Computing Applications
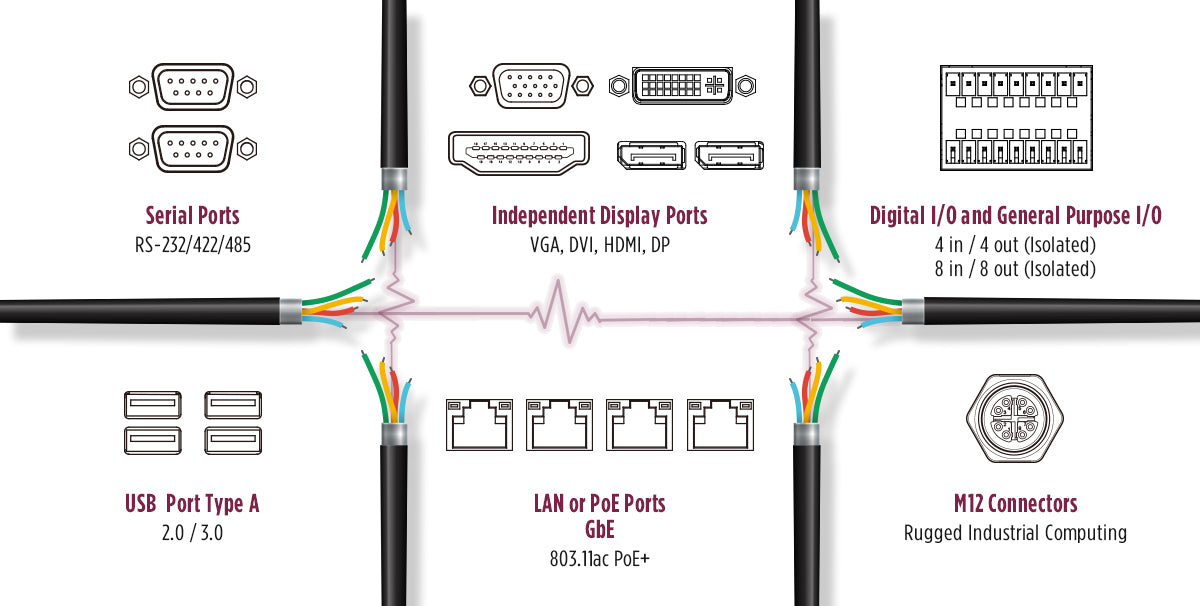
As technological advances in IoT, Big Data, and Machine learning put greater demands on industries like manufacturing and automation, there continues to be a major shift of data and its value across IT and OT efficiencies. In this era of transformation, or what being called “industry 4.0,” more and more devices are being connected to machines; putting an enormous amount of pressure on computing systems to be versatile in its specific functions and workload performances. For example, industrial computers now act as platforms for specific workload consolidation and convergence at the local or edge level. In other words, industrial computing systems now need to be able to manage a variety of data inputs that transmit valuable information for real-time decision making. Therefore, industrial computers support a variety of legacy and new input and output (I/O) ports. Here are some of the most popular I/O ports used in industrial computing deployments today:
Popular Input and Output Ports for industrial computing devices in machine automation
-
Serial ports are the most common port used for an industrial computer. They are used to communicate with legacy devices that are still being used in factories today. While it doesn’t have the fastest data transmission rate, it has been proven to be a reliable protocol over may decades. The legacy serial port has three different modes of function, RS-232/422/485, that vary depending on the application and devices connected.
-
Video ports are required in order to display an output. Some of the most common types of video ports are the VGA, DVI, HDMI, and DP. The VGA port is often used because it uses analog signals instead of digital ones, allowing for connections with legacy devices. Meanwhile the more modern DVI, HDMI, and DP ports lack the legacy compatibility but offer better maximum resolution and refresh rates.
-
DIO/GPIO are acronyms for digital I/O and general purpose I/O. These are forms of interface used for electrical devices or sensors that lack a common interface. The DIO/GPIO uses digital signals with two possible values generally represented as either ON or OFF. This makes them ideal for sensing switch contacts in industrial settings where many ON/OFF signals need to be sent and received. They can be used in a wide range of applications from alarm sensors to automated production lines.
-
USB ports have become the standard port for many devices as the need for more bandwidth increases, which is just not supported by the serial port. Its intelligent power management capabilities allow you to put devices to sleep when not in use, allowing you to connect multiple USB devices without overconsuming power. But it's not the be-all and end-all solution for every industrial computer because depending on the application, both legacy serial ports and USB ports may be required.
-
Local Area Network (LAN) ports provide a wired network connection up to 1GbE per port. Most industrial computers offer LAN ports that are used to provide uplink and downlink for data from a network infrastructure, providing the necessary data transmission from modems, computers, switches, and routers.
Expert Engineering Tip: For those super heavy duty industrial applications, most I/O ports can be configured with rugged M12 locking connectors for even more durability. Contact Premio's industrial and embedded computing engineers for more information. Contact Us!
But What are M12 Connectors and its Benefits in an Industrial Computer?
- M12 connectors are dust and water proof connectors and cables designed to be used in rugged environments where consumer-grade connectors will cause failure. The M12 connector is a favorite in many industries like food processing, beverage manufacturing, vehicle and transportation applications for its robust durability and reliability. This circular connector has a built-in lock mechanism designed to be IP 65 rated or above for rugged water resistance and dust-proof protection from devices to computing machines.
Six Real-World Use Cases that Benefit from Industrial Computers?
1. Manufacturing and Industrial Automation
Industrial computers are ideal for large scale manufacturing that exceeds the physical imitations of human labor. With their robust build and resistance to environmental factors, industrial computers are relied upon by factories to safely handle automated manufacturing and assembly. In most automation and manufacturing settings, industrial computers are used to manage motion control systems for data logging, inspection, and analysis for better manufacturing productivity. For example, the automotive manufacturing industry has greatly benefited from the development of industrial computers due to its level of automation required. The ability to monitor day-to-day functions, track assets, and analyze data make them an essential requirement in this new industry 4.0 landscape.
Interactive kiosk can be found in your local supermarket, large businesses, and even in airport check-in areas. In recent years, this all-in-one computer system equipped with a fanless industrial computer and interactive HMI has shifted from a novelty to an essential business resource. The compact size and rugged features are designed to endure the rigors of various outdoor environments where constant supervision is unavailable. Many new and emerging markets are beginning to embrace machine automation and self-service kiosks as a means of reducing staffing costs and improving overall customer satisfaction.
3. Automation Inspection, Metrology and Testing Equipment
Industrial metrology is the application of measurements for manufacturing and quality control; Or more specifically, how digital measurement instruments can be utilized to ensure quality in the manufacturing process. Traditionally, quality inspection for parts during the manufacturing process was achieved with small batch sampling to determine overall quality. Today, industrial computers are being integrated with more automation capabilities to ensure even more precision and quality of parts. Also with the combination of machine vision, industrial computers are capable of inspecting components faster and more accurately compared to legacy inspection processes . This creates a more efficient and effective manufacturing process and reduces the number of defective products from going to market, creating better value and productivity for manufacturing.
Industrial computers have also been designed for in-vehicle deployments in tough compact conditions such as public transportation and security. Some of the key features like wide temperature support and resistance to shock/vibration are critical for in- vehicle deployments. Industrial computers can also support multiple PoE ports that provide stable connections to IP cameras, which records video footage and improves passenger safety. Ultimately, the fanless rugged design of industrial computers makes it ideal for deployment in rugged surveillance applications.
The harsh nature of underground mining requires specially designed computers able to withstand the demanding conditions characterized by dust, wide temperatures, and vibrations. Industrial computers are extremely robust and can operate in the harshest outdoor environments. These key features are highly beneficial for underground mining equipment because it provides mission critical performance, allowing to capture valuable telemetry for construction and digging sites.
6. Maritime and Military
Military and marine personnel require rugged industrial computers capable of surviving the tough operating conditions on shipboard and ground control operations. Their low maintenance and long operating life meet the requirements and schedules of military operations Additionally, the ruggedized industrial computers can be customized to be fully dust and water resistant to be equally effective across various military applications.

Premio's Industrial Computers
Premio takes the guesswork out of searching for the most appropriate industrial computer by engineering and designing a variety of rugged industrial computing solutions per customer requirements. Each family is purpose-built and validated to ensure high performance and reliability in many industrial applications. With United States product support, customers have turn-key flexibility to fit their special needs.
Premio portfolio of industrial pc and embedded computers
Premio’s fanless mini PCs are designed for entry-level industrial automation that require low costs and minimal power consumption. The minimalistic design keeps the essential I/O ports and offers universal expansion slots for supplemental configurations for additional I/O ports . The rugged, fanless industrial computers are a more robust fanless computing solution for industrial applications where performance and mission critical reliability are equally important. The in-vehicle computer series is specially designed to cooperate with vehicle sensor protocols like CANBus and is validated to operate in a variety of transportation applications. The machine vision computer supports multiple PCIe/PCI expansion slots and digital I/O functionalities to ensure high quality images and accurate interactions with computer vision sensor devices. Lastly, the waterproof industrial computers are IP rated 65/67 rated and offer robust M12 connectors that make them ideal for applications where water and dust may cause harm to the internal functions of a computer.
Contact Premio engineers to learn about the best industrial computer configuration for your specific deployment.