What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a computing framework that brings computing power and storage closer to the edge of a network where data generation occurs and people need to make data-driven decisions. Bringing edge computing devices closer to the source of data generation delivers substantial business benefits, including real-time data analysis and processing, as well as improved response times and increasing the amount of available bandwidth. If properly deployed, edge computers have the ability to enhance the efficiency of processes, automate tasks, and create an overall better customer experience.

Why is Edge Computing Increasing in Importance?
Edge computing devices are increasing in importance thanks to the explosion of data that’s generated from the ever-increasing number of IoT devices. The data generated from IoT devices will continue to grow as more IoT devices come online due to the expansion of 5G networks, bringing more IoT devices online than ever before.
In the past, cloud computing and massive data centers were seen as the solution to coping with the large volumes of data that were generated. However, as more devices come online, data centers will be unable to cope with the huge increase in data volumes, thus necessitating edge computers to relieve the stress placed on them.
This is so because sending every piece of data that is generated by an IoT device to a centralized data center or the cloud for analysis and processing results in overutilization of bandwidth resources and latency issues.
Edge computing solves both of these problems by processing and analyzing the data locally where the data is generated, thus eliminating the need to send all raw data to data centers and the cloud for processing and analysis. This frees up bandwidth and allows the data to be processed in real-time locally, resulting in faster decision-making, faster response times, and improved user experience.
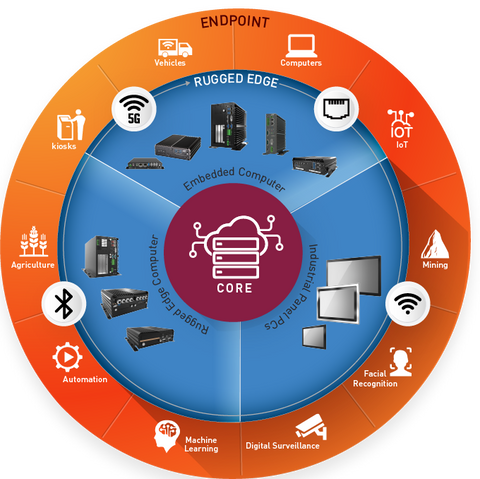
What are the Different Types of Edge Computers?

Edge computing devices come in a variety of different types that include fanless edge computers and rugged edge computers. Today, we will focus this post on rugged edge computing devices, which are compact computing devices engineered and built to operate in the world’s harshest environments.
Rugged edge computers are rugged fanless mini PCs that can survive environments where they will be exposed to frequent vibrations, shocks, dust, debris, extreme temperatures, and much more.
Rugged edge PCs are engineered and built without moving parts. Also, they have a higher temperature tolerance, which allows them to be deployed in environments where regular desktop PCs cannot survive.
Additionally, rugged edge PCs are compact, making them great for deployment in space-constrained environments. For example, the RCO-1000 Series of rugged edge computers comes in at 150 MM (W) x 105 MM (D) x 37 MM (H), making it small enough to fit in the palm of your hand.
Not only are rugged edge computers compact, but they are also rich with connectivity options, allowing the devices to be deployed in remote environments where steady internet connectivity is not always available.
Furthermore, rugged edge PCs come equipped with remote management capabilities thanks to Intel’s vPro platform, enabling remote monitoring and management capabilities, allowing operators to troubleshoot, update, and repair rugged edge computing devices remotely without having to travel to the location of the device.
For more information on the different type of edge computers and an helpful infographic please see a previous blog about "Different Types of Edge Computers."
What are The Benefits of Edge Computing?
Here are some of the advantages that edge computing has to offer:
#1 - Ultra-Low Latency
One of the most significant benefits of edge computing is the ultra-low latency that it provides. There is no doubt that the cloud offers robust, scalable, and powerful data storage, processing, and analysis; however, since data often need to travel thousands of miles to a data center, there are latency issues associated with using the cloud. This is where edge computing comes in.
Edge computing enables applications that require real-time processing and analysis. Take, for example, autonomous vehicles; they must make real-time decisions in order to avoid colliding with other objects. Relying on the cloud to process and analyze the data coming from the various sensors on the vehicles takes a few seconds, which can cause collisions.
On the other hand, Edge computing devices enable real-time decision-making because data does not need to travel long distances for processing and analysis. This is so because edge computing devices are placed close to the source of data generation, permitting data analysis and decision making to be performed locally, in as little as a single millisecond.
#2 - Reduction in Bandwidth
Edge computers are able to reduce the amount of bandwidth required to process and analyze data. This is so because most of the raw data is fed to edge computing devices is processed and analyzed locally, eliminating the need to transmit all of the data to the cloud for processing and analysis.
Instead, edge computers process and analyze the data, only sending data that sets of certain trigger(s) to the cloud for post-processing and analysis. This saves organizations a significant amount of internet bandwidth since only a small amount of data is sent to the cloud for analysis and remote monitoring.
The cost of bandwidth for large scale data transfer can add up, especially if an organization is on a metered data plan, paying for the bandwidth that they use—as such, deploying computers at the edge reduces the cost of bandwidth.
Take, for example, a surveillance system. Traditionally, the entire video feed was sent to the cloud for processing and analysis. Edge computers improved this process by processing and analyzing the video feeds locally, only sending data that set off specific triggers to the cloud for post-analysis and review.
#3 - Service Enhancement
The deployment of edge computers reduces the latency associated with accessing, processing, and analyzing data. Also, it permits the consumer to interact directly with IoT devices bypassing the cloud entirely. This allows businesses to offer a seamless customer experience, which allows organizations to acquire more customers and increase customer engagement while reducing their marketing campaign costs.
What is Rugged Edge Computing?
Rugged edge computing refers to the deployment of ruggedized computers at the edge of a network. Computers at the edge must be rugged because such deployments are typically made in environments that experience challenging conditions, which makes them unfriendly to regular, consumer-grade desktop computers. Rugged edge computers have been engineered and built to bring compute and storage power wherever it needs to be, regardless of how challenging the environmental conditions.
Premio Rugged Edge computers sit at the rugged edge for data processing, storage, and telemetry to and from the cloud
Here are the reasons why rugged edge computers can be deployed in harsh environments.
#1 - Dust & Debris Protection
The main benefit of edge computing devices is the dust and debris protection they provide thanks to their ventless and fanless design, eliminating dust and debris’ introduction into the system. Instead of using fans to cool down the internal heat-generating components, edge computers utilize heatsinks to transfer heat away from the internal components to the system’s outer enclosure, which dissipates the heat into the air surrounding the edge computing device.
#2 - Extreme Temperature Tolerance
Rugged edge computing hardware is able to tolerate scorching hot and freezing cold temperatures thanks to its fanless design. Edge computers have a wide temperature range that ranges between -40⁰C to 85⁰C, allowing edge computers to be deployed in environments that experience extreme temperatures, such as in digital signage in Sweden during the winter where the temperature reaches -30⁰C or an oil field in the middle of the Sahara Desert during the summer where the temperature often exceeds 50⁰C.
#3 - Shock & Vibration Resistance
Another benefit of deploying edge computers is their ability to withstand frequent exposure to shocks and vibrations, something that regular desktop PCs cannot endure. Additionally, rugged edge computing devices adhere to the testing guidelines for military specifications (MIL-SPEC-810G), which guarantees that the rugged edge PC can withstand up to 50Gs of shock and 5GRMs of vibration.
Rugged edge computing devices are able to handle frequent exposure to shocks and vibrations because they utilize a single-piece design that reduces the number of joints, creating a more reliable and robust system. The fewer moving parts an edge computer has, the fewer parts that can fail.
Additionally, eliminating cables from the system creates a solution that eliminates the possibility of a cable coming loose, rendering the system inoperable. By eliminating cables, edge computers are better able to handle exposure to shocks and vibrations, making the systems more reliable and robust.
Furthermore, rugged fanless computers can be configured with SSDs. SSDs create a more rugged edge computing solution because they utilize silicon chips to store data instead of the spinning platters that are used to store data in regular hard drives. So, if you want the most robust solution, you should configure your rugged edge computing solution with SSDs (solid-state drives) instead of HDDs (hard drives).
#4 - Silent Operation
Another advantage of deploying an edge computing device is its ability to operate silently. The elimination of fans and hard drives from the system permits them to operate silently, making them ideal for deployments in environments where silence is required, such as operating rooms, libraries, vehicles, and many more places that require silence.
#5 - Low Power Consumption
An additional benefit of deploying edge computers is their low power consumption. Edge computers are able to use less power than regular desktop PCs because they’re equipped with low-powered CPUs that use little electricity. These devices’ lower power consumption makes them ideal for deployment in environments that don’t have stable power.
This is so because the devices can run off of battery power for prolonged periods of time. Additionally, since they use less power, you will see savings on energy costs. Although the money saved from deploying a single mini edge pc is negligible, you will notice significant savings on energy costs if you’re deploying hundreds or thousands of these devices.
#6 - Robust I/O and Wireless Connectivity
Rugged edge computers come equipped with robust I/O that allows you to connect displays, storage devices, sensors, and other devices via USB 3.1 Gen 2, USB 2.0, HDMI, DP, and COM ports. Additionally, edge computing devices all come equipped with RJ45 LAN ports capable of speeds of up 10 gigabits per second using standard copper cables, with a maximum cable length of 100 meters or 328 feet.
When it comes to wireless connectivity, edge computers can be configured with Wi-Fi 6, 4G, LTE, and 5G for ultra-fast, low latency connectivity. Furthermore, Wi-Fi 6 has a great range and rich features that allow the user to configure Wi-Fi according to your specific requirements.
In the event that Wi-Fi and wired connectivity are not present, your edge computing device can still connect to the internet thanks to built-in SIM slots that enable cellular connectivity, including 4G, LTE, and 5G connectivity options.
Additionally, edge computers come equipped with Bluetooth for quick and simple connectivity with low powered devices. Although Bluetooth does not offer the range and speed that Wi-Fi and cellular connectivity offer, it does provide reliable one-to-one or many-to-many connectivity.
#7 - Small Footprint
Rugged edge computers have a small footprint, which allows them to be deployed in space-constrained environments. The engineers and manufacturers of small edge computers designed them to minimize the amount of space that is taken up by the system, enabling them to fit in small spaces that regular desktop computers cannot fit in.
This makes deploying edge computers in limited-space environments, such as in small cabinets, underneath tables, on walls, or on ceilings, possible. For example, the BCO-1000 Series comes in at 142MM (W) x 101MM (D) x 30MM (H), and the RCO-1000 Series, which comes in at 150MM (W) x 105 (D) x 37MM (H). Both options are compact enough to fit in the palm of your hand.
Cloud Computing vs. Edge Computing?
Cloud computing involves the delivery of computing services, such as storage and computing power over the internet, allowing users to access services using their own computer from anywhere around the world without having to invest in the infrastructure required to store and process their data.
Instead, the individual or organization pays to use centralized cloud computing services which are located in massive data centers across the globe. The organization can choose the appropriate amount of resources it needs, such as computing power, storage, and bandwidth, only paying for what it uses.
On the other hand, edge computing is more decentralized and involves the deployment of edge computing devices at the edges of a network. The edge computing devices are placed close to the source of data generation to process data locally. Edge computing has enabled mobile computing as well as IoT technologies.
In the past, edge computing was not robust and reliable due to the limitations imposed by the low processing power and unavailability of robust storage solutions that can handle the huge volumes of data that were being generated. However, as computer processing power increased and massive amounts of high-speed storage became more accessible and affordable, edge computing has taken off.
The biggest advantage that edge computing has over data centers is that it solves the latency issues associated with cloud computing. Latency issues arise in cloud computing because data must often travel thousands of miles from the origin device to a data center to be processed and analyzed.
Although this is not a problem for someone editing a document in the cloud, the seconds it takes to transfer data to/from the device of origin makes it impossible for applications that require real-time analysis and decision making to run properly. As such, cloud computing solves the latency issues since the computing power is located close to the source of data, analyzing data, and making decisions in real-time.
Edge Computing & IoT
Millions of IoT devices are coming online every day; with the increases in IoT devices comes an increase in the volume and velocity of the data generated by these devices. Data centers are massive, but they will not be able to cope with the massive influx of data that is generated by IoT devices. This is where edge computing comes in.
Edge computing will be able to alleviate the stress placed on data centers by the massive increase in the volume of data by processing data locally. This reduces the amount of raw data that must be sent to the cloud for processing. Instead, edge computers process the data locally and only send data that set off certain triggers to the cloud for post-processing and remote monitoring.
By sending only processed and relevant data to the cloud, you are not only reducing the stress on data centers, but you are also freeing up large amounts of bandwidth that would have otherwise been used to send raw data to the cloud for processing and analysis.
Additionally, by reducing the bandwidth required, you are reducing the costs associated with transferring large volumes of data to/from the device of origin. This is especially important if the IoT devices are on a metered internet connection where the user or organization pays for the amount of data it uses.
The availability of 5G will further increase the number of IoT devices, driving the need for edge computers to cope with data increase. Also, 5G will increase the number of autonomous vehicles, increasing the demand for edge computers to run machine learning and inference algorithms at the edge to guide autonomous vehicles in real-time. Overall, the two major benefits of edge computing vs. cloud computing is the low latency, high bandwidth computing that edge computing offers.
How will Edge Computing Impact Data Centers?
The cloud still has its place in today’s world thanks to the vast amounts of computing resources that can be accessed via the press of a button, removing the need for organizations to invest large sums of money establishing and expanding their infrastructure to gain access to compute power and storage, providing for great and seamless scalability.
That said, although the cloud has solved many problems, the rise of IoT and 5G means that data centers cannot keep up with the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices.
Additionally, AI and automation are increasing the adoption of edge computing because large volumes of data must be stored, processed, and analyzed in real-time. Edge computing makes the process simpler and quicker since data no longer need to travel thousands of miles to data centers, allowing organizations to act smarter and faster.
As the number of IoT devices increases and the need for real-time analysis become more important, so does the need for data centers to become more decentralized, placing more data centers closer to highly populated areas, such as cities and business areas. The closer the data center is to an organization, the less latency the user will experience, and the better the performance.
What Are Some of the Challenges When Deploying Edge Computers?
One of the main challenges of deploying edge computers is that the edge computing device must be rugged. Most edge computing devices are deployed in volatile environments where they are exposed to shocks, vibrations, dust, debris, and extreme temperatures.
This necessitates that edge computers be ruggedized, so that’s exactly what Premio has achieved with its large variety of rugged edge computers that it offers. Rugged edge computers utilize passive cooling, which eliminates the need for vents and opening to circulate air, thus creating a totally closed system that’s protected from dust, dirt, and debris.
Additionally, rugged edge computing devices are equipped with SSDs, which are far more reliable than traditional hard drives that use spinning platters to store data. Instead, SSDs store data on silicon chips, which are less prone to damage when exposed to shocks and vibrations.
Furthermore, rugged edge computing devices can be deployed in environments that experience extreme cold or extreme heat thanks to the industrial components that are used to manufacture rugged edge PCs, allowing them to operate in cold environments where the temperature reach -40⁰C and extremely hot environments up to 85⁰C.
The second challenge of deploying rugged edge computers is that oftentimes, tens, hundreds, or even thousands of devices have to be deployed, and so servicing and maintaining so many devices becomes difficult. However, rugged edge computers come equipped with the Intel vPro Platform.
The vPro platform provides IT professionals with the ability to remotely manage and repair PCs, interactive kiosk machines, digital signage, surveillance systems, and much more, even when the devices are powered off. The vPro platform reduces the cost of maintaining edge computer systems and lessens interruptions to the services provided by your business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the meaning of edge computing?
Edge computing means that a computing device, often known as an edge computer, is placed at the source of data generation. For example, suppose a beverage processing plant needs a computer to collect sensor data and analyze it. In that case, an edge computer can be placed at the plant close to where the sensors are gathering the data. In this case, the computing device would be an edge computing device. This should help clarify the definition of edge computing.
2. Why is Edge Computing Faster Than Cloud Computing?
Edge computing is faster than cloud computing because data does not need to travel thousands of miles to data centers for processing and analysis. Instead, edge computers are placed closed to the source of data generation for real-time processing and analysis. For example, it would take a few seconds for an IoT device to send sensor data to the cloud for processing and having the processed data analyzed and sent back vs. edge computing, which can process and analyze the data in a few milliseconds by eliminating the need for information to travel through networks.
3. What are some popular examples of edge computing?
Some examples of edge computing include the edge computing system used to power interactive kiosk machines, surveillance systems, security systems, digital signage, autonomous vehicles, factory automation system, and many more use cases. That said, each of these use cases requires a different type of edge computer that can handle the tasks it needs to accomplish. For example, an edge computer deployed to power digital signage does not need to be as powerful as an edge computer deployed to power an autonomous vehicle.
4. What does the future of edge computing look like?
The future of edge computing looks promising because as more and more IoT devices come online and 5G expands internet access to more people, edge computers will be necessary to alleviate some of the burdens placed on data centers due to the large volume and velocity of data that’s produced. Some experts believe that edge computing hardware is expected to grow from $2.8 billion in 2019 to $18.36 billion in 2027.






